The rise of GLP‑1 therapies has reshaped the management of obesity and metabolic disease, yet a growing wave of duodenal resurfacing devices is emerging to help sustain weight loss beyond drug discontinuation. At the same time, Pharma patents remain central to how companies defend innovation, set pricing, and shape access to both GLP‑1 drugs for weight loss and novel devices. This article explores the scientific rationale, clinical evidence, competitive landscape, regulatory strategies, and intellectual property implications, including pharmaceutical patents list, list of pharma patents, and broader patents in pharmaceutical industry trends, for stakeholders navigating this evolving field.
Introduction: Why GLP‑1 Transformation and Device Innovation Matter
Since their introduction, GLP‑1 receptor agonists, like semaglutide and GLP‑1 tirzepatide have rapidly become leaders in GLP‑1 weight loss therapy by promoting appetite suppression, delaying gastric emptying, and improving insulin sensitivity. Many patients experience meaningful weight loss outcomes on these medications, yet continuing treatment is often required to maintain results. This has consequences:
- High GLP‑1 cost, influenced by exclusive patent protection and limited competition, restricts access for many patients.
- GLP‑1 side effects: which commonly include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea that have lead some patients to discontinue therapy early.
- Potential generics are on the horizon, including GLP‑1 pills and GLP‑1 oral solution formats that may change prescribing patterns and access.
This creates strategic opportunities not only for physicians and patients, but also for innovators developing supplemental or alternative weight‑management solutions, particularly those that might extend or lock in benefits after drug withdrawal.
How Duodenal Devices Work to Sustain Weight Loss
Emerging duodenal remodeling technologies focus on the duodenum, the first segment of the small intestine immediately distal to the stomach. It is a physiological hub for nutrient sensing and enteroendocrine signaling that plays a critical role in metabolic regulation. These devices aim to reset dysfunctional mucosal signaling, especially pathways influencing insulin resistance and satiety without surgery.
Most approaches share common principles:
- Primary site of action: Duodenal mucosa (epithelium and superficial lamina propria)
- Goal: Controlled disruption and regeneration, preserving motility and avoiding deeper muscular injury
- Procedure: Outpatient, endoscopic delivery
Hydrothermal Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing
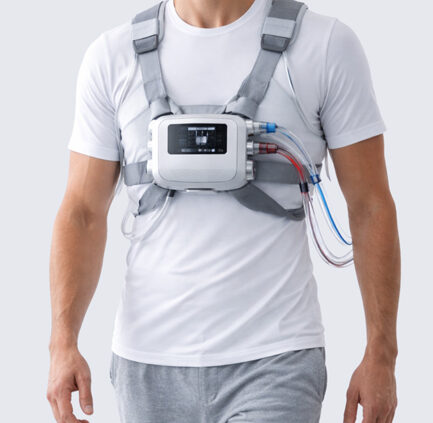
Hydrothermal ablation uses controlled heat to selectively remove the surface mucosa, prompting regeneration. Fractyl Health’s Revita is the leading example of this method, with a robust patent portfolio that includes multiple issued device and method patents covering energy delivery systems and catheter configurations. These Pharma patents bolster its competitive position.
Revita’s procedure is being studied in pivotal trials designed to evaluate sustained weight loss after patients stop GLP‑1 medications, a strategic regulatory pathway that reflects the real clinical need for post‐pharmacotherapy.
Pulsed Electric Field Ablation
Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) technologies use non‑thermal electrical pulses to ablate dysfunctional cells while preserving collagen and nerves. Dose and waveform control are key differentiators in this modality, and early studies suggest improvements in insulin sensitivity and metabolic markers.
Radiofrequency Vapor Ablation
Radiofrequency vapor ablation (RFVA) delivers controlled thermal energy via catheter to ablate mucosal tissue. Emerging platforms from companies like Aqua Medical are in early clinical and regulatory planning stages.
Duodenal Liner Technologies
Endoluminal duodenal‑jejunal bypass liners (e.g., RESET/DJBL) create a temporary physical barrier that mimics the intestinal bypass effect of surgical procedures, bypassing nutrient contact in the duodenum and proximal jejunum.
Laser Resurfacing
Laser‑based systems are early in clinical translation and offer precise control over mucosal ablation via endoscopically delivered laser energy.
All approaches aim to harness the duodenum’s role in nutrient sensing to support metabolic homeostasis and long‑term weight loss outcomes.
Evidence and Regulatory Status Across Device Types
Although evidence is still emerging, pilot studies and early pivotal programs show encouraging signals:
- Fractyl’s Revita has received FDA Breakthrough Device designation in weight maintenance for people with obesity after discontinuation of GLP‑1 therapy and continues enrollment in key pivotal trials.
- PEF and RFVA platforms are advancing through regulatory interactions to support robust U.S. clinical trials.
- Liner technologies have obtained CE marking and are commercially available in select markets.
The weight loss field generally recognizes that robust randomized evidence, comparative effectiveness trials, and longer‑term safety data will be crucial for guideline adoption and payer coverage.
The Competitive Landscape: Who’s Building What
The duodenal device market is heterogeneous, with multiple innovators pursuing distinct technical approaches:
- Fractyl Health (Revita) – Leader in hydrothermal duodenal mucosal resurfacing with a strong IP portfolio.
- Endogenex (PEF) – Focuses on pulsed electric field biologically selective ablation.
- Aqua Medical (RFVA) – Developing radiofrequency vapor ablation technology.
- Morphic Medical (RESET/DJBL) – Commercializes duodenal‑jejunal bypass liners.
- TeCure and Other Laser Platforms – Early‑stage development in laser‑based resurfacing.
Each company’s approach has different regulatory and commercialization pipelines, but all converge on harnessing duodenal physiology for metabolic benefit.
GLP‑1 Drugs and Patent Protection
While devices represent a complementary innovation axis, GLP‑1 drugs remain the dominant force in current anti‑obesity therapy. Semaglutide (e.g., Wegovy) and tirzepatide (e.g., Mounjaro/Zepbound) have demonstrated clinically meaningful weight loss, prompting both enormous demand and scrutiny over pricing.
Patent Strategies and Protection
Brand‑name manufacturers often deploy layered patent strategies to extend exclusivity and delay generic competition. On average, GLP‑1 receptor agonists have nearly 20 individual patents associated with each product, with over half focused on delivery devices rather than the active ingredient itself.
This strategic layering includes:
- Composition and peptide sequence patents
- Delivery device patents (e.g., pens, injection systems)
- Formulation patents and dosing regimens
- Secondary method‑of‑use patents
Compounded by regulatory exclusivities, these tactics help maintain high prices and long periods of market control. The median effective patent protection duration for GLP‑1 drugs can exceed 18 years from approval.
Patent Timing, Generics, and Market Evolution
Semaglutide core patents are set to expire around March 2026 in several emerging and regulated markets, which has triggered a global race among companies (like Dr. Reddy’s, Cipla, and Sun Pharma) to prepare generic or biosimilar versions.
However, secondary patents, such as those on delivery or formulation, may extend exclusivity into the 2030s. For example:
- Tirzepatide core compounds may see expiry in the mid‑2030s, with additional patents potentially pushed into the early 2040s.
New Formats: Pills, Oral Solutions, and Supplements
The GLP‑1 market is evolving beyond traditional injectables:
- GLP‑1 pills now exist, such as pill formulations of Wegovy approved in the U.S., offering alternatives to weekly injection.
- GLP‑1 oral solution formats are also gaining traction.
- Some consumer products market themselves as GLP‑1 supplements, but patients and clinicians should be cautious, as many lack robust clinical evidence and are not regulated as drugs.
Generic and alternative formulations may expand access and broaden patient choice, especially if they carry lower pricing and fewer barriers.
Pharma Patents and Industry Dynamics
Understanding patents is essential for investors, dealmakers, and industry strategists. Key points:
Freedom‑to‑Operate and Patent FTO
Device innovators must navigate existing patent thickets, which often include patents on catheter designs, energy delivery parameters, and method claims, areas that overlap with traditional GI intervention technologies.
Mapping foundational patents and conducting drug patent search exercises are critical to avoid infringement and inform licensing or acquisition decisions.
Pharma Patent Professional Roles
The intersection of drug and device IP has given rise to specialized roles:
- Patent attorneys and agents with expertise in both device and biologic domains
- Regulatory strategists versed in pharmaceutical patent law salary expectations aligned with life‑science markets
Understanding compensation trends and market demand for IP expertise helps companies plan competitive IP teams.
Access, Pricing, and Policy Challenges
Despite strong efficacy, GLP‑1 therapies have faced criticism for affordability. High GLP‑1 costs are enabled by robust patent protections that delay generic entry, keeping prices high in many markets.
Government negotiations, like recent U.S. policy initiatives to reduce weight‑loss drug prices, aim to expand access by lowering out‑of‑pocket costs.
Meanwhile, advocates argue that timely access to generics and improved guideline coverage is needed to avoid inequities in obesity care.
Patent Drugs vs Generic Drugs: The Value Debate
The debate over the type of drug often centers on balancing innovation incentives with affordability and access. Brand‑name patents fund discovery and safety testing but can also delay affordability. Conversely, generics increase competition and lower prices but come with challenges related to manufacturing complex biologics.
For GLP‑1 receptor agonists, much of this debate will unfold in the next decade as major patents expire, and new formats enter the market.
Future Outlook: Devices, Drugs, and Integrated Approaches
In the next 18–36 months, the obesity treatment landscape is poised for meaningful change:
- Device innovators advancing duodenal remodeling technologies may unlock sustainable weight loss strategies complementary to pharmacotherapy.
- Evolving GLP‑1 pills and oral formulations may broaden reach.
- Generics and biosimilars will reshape GLP‑1 cost dynamics.
- Strategic use of Pharma patents, both in devices and drugs will determine competitive leadership and partnership opportunities.
Companies that combine robust clinical evidence, disciplined regulatory strategy, and a defensible, layered IP posture will likely emerge as leaders. For patients, these innovations promise expanded options tailored to cost, convenience, and long‑term outcomes.