Metaverse can be described as living in the Internet; interacting with and in a computer-generated virtual environment which is consistently tethered to the internet. It can almost be said that Metaverse gives one an opportunity to escape their real-life; to explore, engage and gain experience that might be improbable without technological interventions like the development of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). Like how the Internet is made up of several web-pages, the Metaverse consists of inter-connected 3D, virtual worlds or environments, hosting games, marketplace, conference rooms, wildlife safari or simple houses where the avatar lives.

The Metaverse was first coined by Neal Stephenson, a science fiction writer in 1992 and since then it has been greatly expanded, where it is no more fiction but a reality. Its first implementation was in video games though it was not as extensive as it is today. Video games providing online multiplayer game modes gave players a cyberspace where they could interact, initially with text chats and later including voice chats, which began to be known as a lobby. These lobbies offered an excellent channel to communicate and socially interact with players across the globe. This not only imbibed increased competition, but also teamwork and co-operation between players aiming for a common objective.
Counter Strike: Global Offensive is one such example. In 2003 when Second Life was released, the partial vision of Metaverse was materialized in an online game, featuring a virtual world where players could create a representation of themselves using avatars and, as the name suggests, live a second life. Players or residents can interact & socialize with each other, build, sell & trade in-game assets or be part of a group activity. There has been a significant shift of focus of Metaverse & proto-metaverse development from gaming; to it being used primarily for social interactions by recreating workspace environment, classrooms, marketplaces and even clubhouse & discos. Expanding horizon for metaverse has seen its expanse in the field of IP and rights. Metaverse being nascent, with promising monetary earnings, establishes a need for regulation in this virtual space as well.
What Metaverse means to TECH GIANTS?
There is a hype surrounding Metaverse and major companies in the forefronts of technical development associated to Metaverse Technology. Be it hardware or software, still in the early stages of conception, there are super exciting advancements in Metaverse technologies from better AR/VR headsets to realistic character & avatar modelling to enhanced controller for a more natural handling experience. Metaverse is an uncharted territory. Its direction of evolving is ungoverned and depends on how the users and the service providers i.e., the tech giants, utilise its potential ranging from gaming, partying & exercising to buying & selling, marketing, conferencing, advertising and a lot more. Metaverse’s success depends on its interoperability between current proto-metaverses, along with regulations on advertising, media, gambling & finances and GDPR to name a few. These tech giants can gain competitive and monetary advantages, if the aforementioned regulations are not enforced.
Top 5 Companies Working on Metaverse
Meta (Facebook) with Horizon Worlds platform, accessible through Oculus Quest VR headset, was rolled out last December. It hit a record 300,000 concurrent users in 3 months. It is Meta’s rendition of the metaverse with around 10,000 virtual worlds created in it. Mark Zuckerberg with upwards of $10 billion investment for developing the metaverse, is definitely betting hard on the success of virtual environments and computer-generated worlds experienced through AR/VR and even extended reality (XR).

Image Source: VRScout, Horizon Worlds is Meta’s take on Metaverse
Roblox has the greatest number of user-generated virtual worlds and games or ‘experiences’, around 24 million, in which players can experience any imaginable scenario. It is community driven with roughly 9.5 million developers and around 50 million active daily users. Its non-dependency on VR headsets and consoles, being able to play on any device has appealed to Gen-Z. Craig Donato, the chief business officer at Roblox believes AR/VR technology is unnecessary for immersion. Hence, they are supporting Guilded and Loom.ai. Roblox planning to include Virtual Assets in-game, showcasing its marketing prospective.

Image Source: VG247, Roblox is very popular among children below 16
Epic Games was one of the first companies to innovate and utilize the potential of Metaverse by hosting in-game musical shows. It started off in 2020 and now is a hit among players of Epic Games owned Fortnite. They have unveiled concert series titled Soundwave. At the end of 2021, a trademark application was filed for ‘Epic Games Megaverse’, which is their take on metaverse. $1 billion funding goal was also achieved in 2021, hinting at the research and development to expand their portfolio beyond gaming.
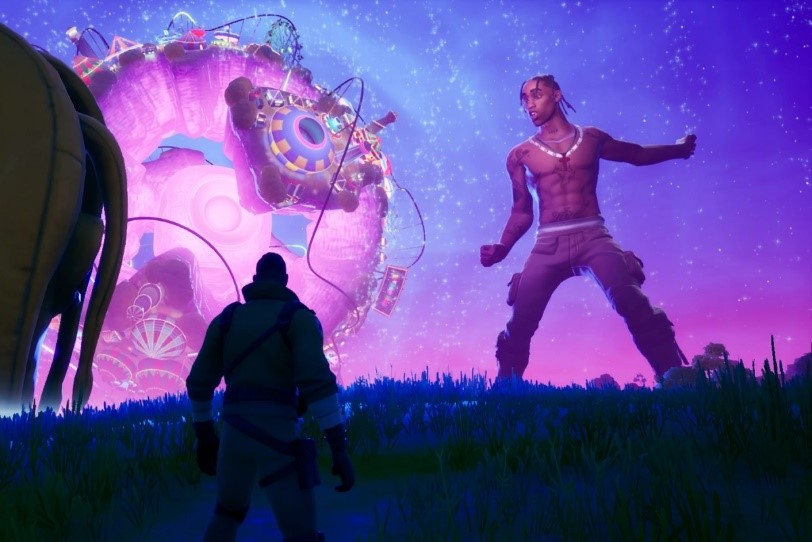

Image Source: Rolling Stones, American rapper Travis Scott performed and presented Astronomical in Fortnite
Nvidia has developed a platform for connecting Metaverse, named NVDIA Omniverse. Omniverse is a 3D design and simulation toolkit. This software was initially launched as a virtual environment builder for engineers. But at the start of 2022, NVIDIA announced free license to artists and creative individuals. It has seen over 100,000 downloads. The gaming industry giant has partnered with 4 online marketplaces and virtual assets libraries to feature Omniverse suite used virtual assets that the creators can sell. This technology is also employed in developing “digital twins’ and running real world simulations.
Image Source: Nvidia, is a powerful software that integrates collaborative works from different platforms
Tencent is the biggest Chinese game publisher and has a dominant presence when it comes to mobile gaming with games like PUBG: Mobile. The secluded and strictly reserved internet in China will prompt the Metaverse to develop according to the government regulations and constraints, where only Chinese tech giant will prosper. In October 2021, news was revealed about Tencent Holdings plans to reorganize TiMi Studio Group into a dedicated metaverse development subsidiary under the intitative named ‘F1’. It is still unclear about the actual reorganization, but whispers from company insider support the claim.

Image Source: Mobidictum, Tencent’s ‘F1’ initiative hints at the company’s interest in Metaverse
Noteworthy Company Collaboration for Metaverse
Roblox and Fortnite partner with NERF (Hasbro) for featured products and virtual assets


Epic Games bagged $250 million investment from Sony as a part of shared aim of 3D virtual spaces

Microsoft to buy Activision Blizzard for $68.7 billion by 2023

Google and North, Inc merger will make smart glasses more advanced

Tencent in talks to acquire Black Shark to expand in AR/VR tech

Microsoft announces Qualcomm collaboration for better Metaverse related AR tech

Meta and VictoryXR join hands to bring immersive learning experiences

Reviewing PATENT DATA provides another perspective
To truly discover the industry competition, going through patent data is the key. This sheds light on those upcoming new and interesting technologies or help understand the extent and reach of the advancements in Metaverse technology.
Companies like Meta Platforms, Inc., Google, Inc., IBM, Microsoft and HTC are rigorously trying to secure technology sets that will fare them better in the race to dominate the Metaverse. After researching the market for patent data, following technologies have seen hits among different tech companies,
- Focusing on augmented reality systems,
- 3D projector and camera systems,
- 3D environment modelling and behavior analysis,
- optical systems with parallax corrections and ultrasonic eye tracking,
- head mounted displays with facial interface & strap and front assembly optimizations; equipped with attention, comprehension and drowsiness monitoring & steering recognition systems,
- behavioral and account fingerprints,
- user experience modifications and multi-axis user interface,
- user tracking with time-of-flight sensors and radar,
- audio augmentations, specializations & enhancements,
- improved wearable controller with gesture detection and wrist tracking will ensure seamless interaction with the virtual world.
- creating database off virtual world,
- developing documents from text in virtual environment,
- methods of social interaction and attending recorded virtual sessions,
- private conversation in public spaces,
- virtual object sharing and watermarking with virtual security to inculcate collaborative workspace ethics.
METAVERSE in the next decade
Metaverse in the current state is much closer to being the real deal, than it was a decade back. Drastic improvements in methods to include various experiences for users, tools to express oneself with avatars and realism of metaverse characters with real-time facial expression mirroring, immersive learning with interactive feedback for improved cognitive abilities, efficient productivity with range of ambient atmospheres are some visions of what Metaverse should become, thereby dominating IT, healthcare, education, real estate, manufacturing, digital advertisements and even military. With these prospects IP themes of Protection, Exploitation and Enforcement will be incorporated meticulously. Continuous research and development in these fields with the integration of AR/VR systems strives for a better Metaverse experience. Chiming in new economy, one that is flooded with virtual assets like digital clothing, NFTs, virtual real estate and lot more; facilitated by cryptocurrencies.
There are immense growth opportunities to flourish at this stage of metaverse. This concept of connected individuals over internet, is a step up from the current social media. But what will data security look like when microchips will be put in our heads, monitoring brain activity, to navigate through the Metaverse? There is uncertainty about privacy. It is unclear how moderation of community will be enforced. If it is, then it will be very intrusive in nature, concerned with smallest of things like a tattoo or an emote of an avatar. There is a high chance of addiction to this virtual self that might not represent the slightest of the real life, developing a false sense reality. Nothing is cogent as of now; the pros do outweigh the cons, but time will tell if the Metaverse is for the better or worst.
FAQs
Q1) What is the Metaverse?
Metaverse consists of inter-connected 3D, virtual worlds or environments, hosting games, marketplace, conference rooms, wildlife safari or simple houses where the avatar lives. It is – interacting with and in a computer-generated virtual environment which is consistently tethered to the internet.
Q2) What does Metaverse look like?
Unlike a physical environment which takes up space metaverse is a computer-generated simulation of an experience, it’s just mere codes running in the computers. Because of the computing power metaverse can morph into any imaginable form. It can be a cyberpunk themed city or ancient Roman city or better, you can place yourself inside a game, if you fancy; the possibilities are endless.
Q3) What is the purpose of Metaverse?
The purpose of the Metaverse is to connect everyone virtually through internet. Metaverse can be described as living in the Internet. It holds the prospect for being the next big thing in the internet, a fully interactable and immersive version of the internet that we know as of now. It can transform the way the we perceive regular activities like working, social gathering, meet-ups, tours, expedition, partying, playing and even relaxing.